The genome, holding the DNA code of each life form, has been shown to be an immensely valuable tool in studying the degree of relatedness among different organisms. Certain genes involved in some of the most fundamental and widely shared processes in living organisms are found in similar forms in a majority of higher organisms. These genes can be sequenced in the laboratory and then compared to get a more quantitative measure of the genetic relatedness of individuals in a population or a group of individuals from different species. With advances in the science of biotechnology, extracting, purifying and sequencing DNA has become faster and less expensive to perform, making it possible to sequence large numbers of specimens quickly and relatively easily. This genetic information adds another important dataset to the other anatomical and behavioral observations that help to make species determinations.
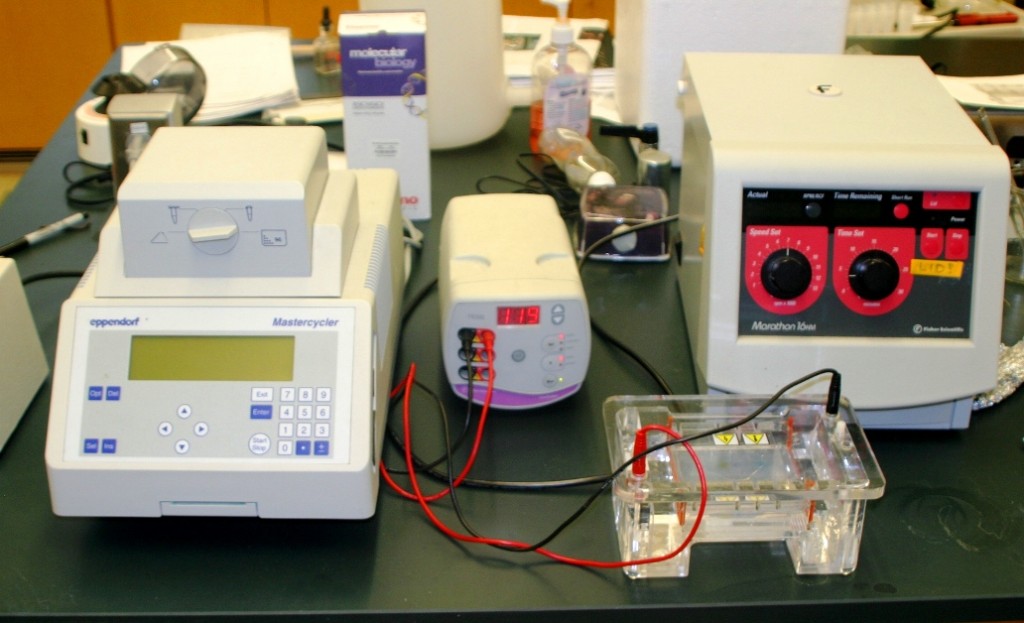
Above, a PCR thermocycler, gel electrophoresis box, and ultracentrifuge used in GSENM Nemoria intensaria DNA amplification and purification.
Software allows researchers to compare large numbers of different sequences at once and identify locations in the DNA where a part of the code (a single base or nucleotide) varies between sequences. One of the most frequently sequenced genes for comparing and even identifying species is called the cytochrome oxidase I gene, or CO-I. This gene produces a protein subunit that is involved in the aerobic respiration pathways of a cell’s mitochondria.
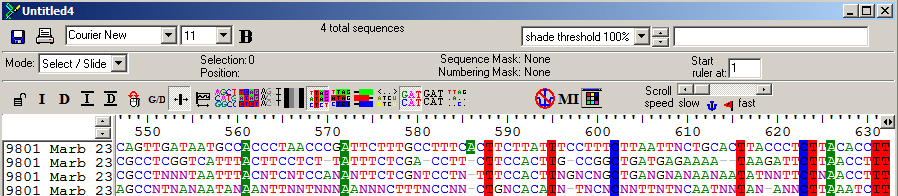
Below, an image of software that shows the alignment of four different DNA sequences with DNA bases (A, T, C, and G) shaded where they are identical across all four sequences.
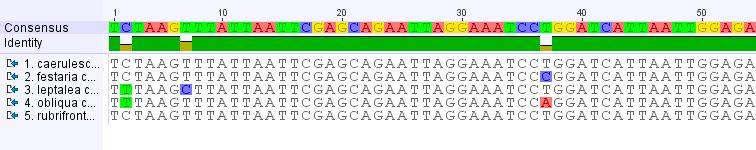
And below, an aligned set of DNA sequences from five closely related Nemoria species, showing the DNA bases shaded in color that vary among these five moths. Note that in the second position, two species have a T (thymine) shaded in green at a location where the other three have a C (cytosine).